

sudo chmod 640 /etc/systemd/system/htg.service This command will give the owner read and write permissions, and read permissions to the group. You don’t want a malicious or mischievous user changing the unit file so that it executes a different program altogether. The unit file doesn’t need to be executable, but the permissions on the unit file should restrict who can edit it. WantedBy: We have this set to “multi-user.target”, which means the service should be started as long as the system is in a state where multiple users can log in, whether or not a graphical user interface is available.If our service was a non-trivial program instead of a simple script, we would set this to “mixed” to ensure that any spawned processes were also terminated. We have this set to “process.” This causes systemd to use the SIGTERM signal on the main process only. KillMode: Defines how systemd should kill the process if we ask systemctl to stop the service.RestartSec: How long to wait before attempting to restart the service.Restart: When and if the service should be restarted.ExecStart: The path to the process that should be started.systemd will consider this service started as soon as the process specified by ExecStart has been forked. After: A list of unit names that should be started after this service has been successfully started, if they’re not already running.Wants: Our service wants-but doesn’t require-the network to be up before our service is started.Description: This is a text description of your service.Our simple service doesn’t actually need most of them, but including them allows us to explain them. Copy and paste the following text into the editor: Īfter=syslog.target network-online.target sudo gedit /etc/systemd/system/htg.service No unit files have that name, so we can proceed and create our unit file. Our service is going to be called “htg.service”. You can scroll through the list of unit files, which is sorted alphabetically, and check that the name you want to use is not taken. sudo systemctl list-unit-files -type-service We need to create a unit file for our new service, but it is prudent to make sure none of the existing unit files have the name we want to give our new service. This holds certain attributes that systemd can use to locate and launch the program, and to define some of its behavior. sudo cp htg.sh /usr/local/binĪnd we need to make it executable: sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/htg.shĮach program that is started by systemd has a definition file, called a service unit file. We’ll copy the script to the /usr/local/bin directory. So, this script writes a timestamped message to the journal once per minute. After 60 seconds the loop is repeated.This is formatted into a message and sent to the journal. The TIMESTAMP variable is set to the current date and time.They’re not important errors or warnings. We’re using the -p (priority) option to indicate that our messages are for information (info) only. Entries to the journal are given a priority. The two echo lines are piped through systemd-cat, a program that takes the output from a program and sends it to the journal.The script doesn’t do a whole lot, but there are a few points worth noting. #!/bin/bashĮcho "htg.service: # Starting #" | systemd-cat -p infoĮcho "htg.service: timestamp $" | systemd-cat -p info Copy and paste the following text into the editor. This tutorial uses the Gedit text editor, but you can use whatever text editor you prefer. We’ll create a simple script, called “htg.sh”. We need to have a program that systemd will launch. Controllable using systemctl, the control interface for systemd.Integrated with systemd through a service unit file.
To tick all the boxes, our service must be: In this article, we’ll create an example service. The “d” at the end of systemd stands for daemon.
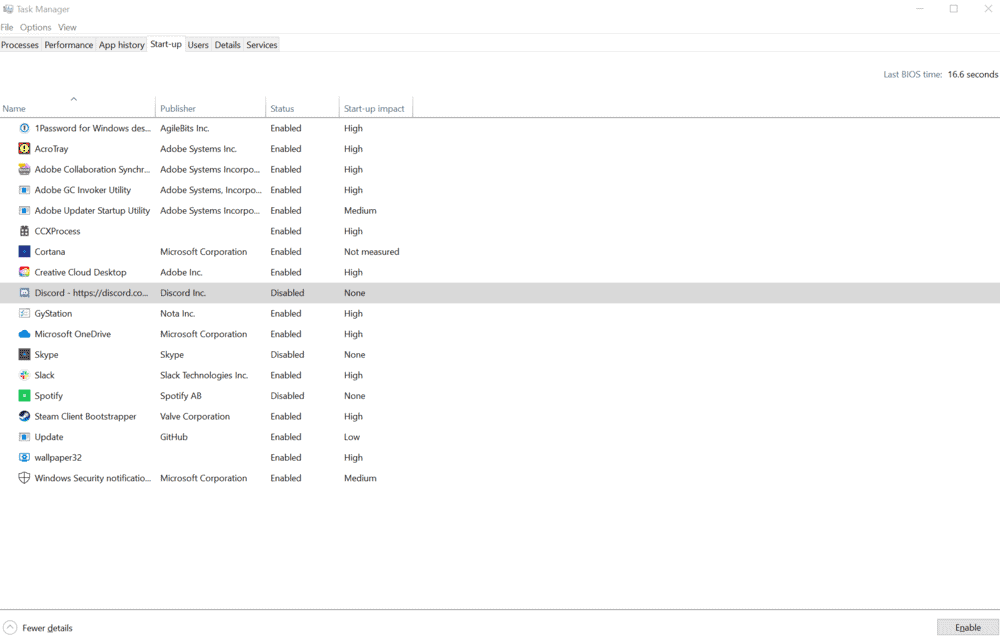
Programs that run in the background are called daemons or services. Every other process running in your computer is started by systemd, or by a process that systemd has already started. systemd is the first process to run at startup. The programs that are launched at startup are controlled by systemd, the system and service manager. You can easily achieve this same behavior with your own programs and scripts, or in fact any other program that is on your computer.
HOW TO START A SYSTEM IN ARC XT PRO INSTALL
Sometimes the software you install on your computer hooks itself into the Linux startup process, so that the program is automatically launched each time the computer is started.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
